Ideal for Spleen Tissue Homogenization
Do you spend lots of time and effort homogenizing spleen tissue samples? The Bullet Blender® tissue homogenizer delivers high quality and superior yields. No other homogenizer comes close to delivering the Bullet Blender’s winning combination of top-quality performance and budget-friendly affordability. See below for a spleen tissue homogenization protocol.
Save Time, Effort and Get Superior Results with
The Bullet Blender Homogenizer
Consistent and High Yield Results
Run up to 24 samples at the same time under microprocessor-controlled conditions, ensuring experimental reproducibility and high yield. Process samples from 10mg or less up to 3.5g.No Cross Contamination
No part of the Bullet Blender ever touches the tissue – the sample tubes are kept closed during homogenization. There are no probes to clean between samples.Samples Stay Cool
The Bullet Blenders’ innovative and elegant design provides convective cooling of the samples, so they do not heat up more than several degrees. In fact, our Gold+ models hold the sample temperature to about 4ºC.Easy and Convenient to Use
Just place beads and buffer along with your tissue sample in standard tubes, load tubes directly in the Bullet Blender, select time and speed, and press start.Risk Free Purchase
Thousands of peer-reviewed journal articles attest to the consistency and quality of the Bullet Blender homogenizer. We offer a 2 year warranty, extendable to 4 years, because our Bullet Blenders are reliable and last for many years.Spleen Tissue Homogenization Protocol
Sample size |
See the Protocol |
| microcentrifuge tube model (up to 300 mg) | Small spleen samples |
| 5mL tube model (100mg - 1g) | Medium spleen samples |
| 50mL tube model (100mg - 3.5g) | Large spleen samples |
What Else Can You Homogenize? Tough or Soft, No Problem!
The Bullet Blender can process a wide range of samples including organ tissue, cell culture, plant tissue, and small organisms. You can homogenize samples as tough as mouse femur or for gentle applications such as tissue dissociation or organelle isolation.

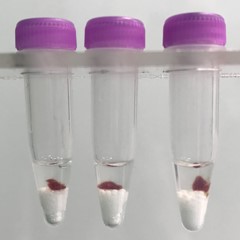

Spleen tissue pieces (on beads in upper photo) are completely homogenized into the buffer (darker in lower photo).
Want more guidance? Need a quote? Contact us:

Bullet Blender Models
Select Publications using the Bullet Blender to Homogenize Spleen Tissue
2474232
spleen
1
apa
50
date
desc
3263
https://www.nextadvance.com/wp-content/plugins/zotpress/
%7B%22status%22%3A%22success%22%2C%22updateneeded%22%3Afalse%2C%22instance%22%3Afalse%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22request_last%22%3A0%2C%22request_next%22%3A0%2C%22used_cache%22%3Atrue%7D%2C%22data%22%3A%5B%7B%22key%22%3A%22DT6T59PN%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Li%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016-04-27%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BLi%2C%20M.%2C%20Li%2C%20C.%2C%20Song%2C%20S.%2C%20Kang%2C%20H.%2C%20Yang%2C%20D.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Li%2C%20G.%20%282016%29.%20Development%20and%20antigenic%20characterization%20of%20three%20recombinant%20proteins%20with%20potential%20for%20Gl%26%23xE4%3Bsser%26%23x2019%3Bs%20disease%20prevention.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BVaccine%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B34%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2819%29%2C%202251%26%23x2013%3B2258.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.vaccine.2016.03.014%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.vaccine.2016.03.014%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Development%20and%20antigenic%20characterization%20of%20three%20recombinant%20proteins%20with%20potential%20for%20Gl%5Cu00e4sser%27s%20disease%20prevention%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Miao%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Li%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Chunling%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Li%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shuai%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Song%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Huahua%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dongxia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Guoqing%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Li%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Haemophilus%20parasuis%20is%20the%20causative%20agent%20of%20Gl%5Cu00e4sser%26%23039%3Bs%20disease%2C%20which%20causes%20high%20morbidity%20and%20mortality%20in%20piglets%2C%20leading%20to%20severe%20economic%20losses.%20The%20lack%20of%20a%20commercial%20vaccine%20against%20a%20broad%20spectrum%20of%20strains%20has%20limited%20the%20disease%20control.%20H.%20parasuis%20outer%20membrane%20proteins%20%28OMPs%29%20are%20potentially%20essential%20components%20for%20vaccine%20formulation.%20In%20this%20study%2C%20seven%20putative%20OMPs%20were%20selected%20from%20the%20annotated%20H.%20parasuis%20serovar%205%20genome%3B%20they%20were%20predicted%20by%20bioinformatics%20and%20annotated%20as%20potential%20virulence-related%20factors.%20These%20proteins%20were%20cloned%2C%20expressed%2C%20and%20purified%20as%20His-tagged%20proteins.%20Antigenicity%20of%20the%20candidate%20proteins%20was%20assessed%20using%20Western%20blotting%20with%20convalescent%20sera%20against%20H.%20parasuis%20serovar%205.%20The%20immunogenicity%20of%20the%20seven%20OMPs%20was%20assessed%20in%20a%20guinea%20pig%20model.%20Except%20VacJ%2C%20all%20the%20other%20six%20recombinant%20proteins%20elicited%20a%20detectable%20antibody%20response.%20Antisera%20against%20four%20of%20the%20selected%20proteins%20effectively%20killed%20the%20bacteria%20in%20vitro.%20Three%20proteins%20%28Omp26%2C%20VacJ%2C%20and%20HAPS_0742%29%20were%20found%20to%20confer%20signi%5Cufb01cant%20protection%20against%20challenge%20with%20a%20lethal%20dose%20of%20H.%20parasuis%20in%20a%20guinea%20pig%20model.%20The%20results%20suggest%20that%20these%20three%20proteins%20have%20a%20strong%20potential%20to%20be%20vaccine%20candidates%20against%20Gl%5Cu00e4sser%26%23039%3Bs%20disease.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22April%2027%2C%202016%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.vaccine.2016.03.014%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220264-410X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0264410X16003145%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-06-24T16%3A30%3A49Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%227Q9J8E8W%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Cole%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016-04-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A3%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BCole%2C%20L.%20E.%2C%20Zhang%2C%20J.%2C%20Kesselly%2C%20A.%2C%20Anosova%2C%20N.%20G.%2C%20Lam%2C%20H.%2C%20Kleanthous%2C%20H.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Yethon%2C%20J.%20A.%20%282016%29.%20Limitations%20of%20Murine%20Models%20for%20Assessment%20of%20Antibody-Mediated%20Therapies%20or%20Vaccine%20Candidates%20against%20Staphylococcus%20epidermidis%20Bloodstream%20Infection.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BInfection%20and%20Immunity%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B84%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%284%29%2C%201143%26%23x2013%3B1149.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1128%5C%2FIAI.01472-15%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1128%5C%2FIAI.01472-15%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Limitations%20of%20Murine%20Models%20for%20Assessment%20of%20Antibody-Mediated%20Therapies%20or%20Vaccine%20Candidates%20against%20Staphylococcus%20epidermidis%20Bloodstream%20Infection%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Leah%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cole%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jinrong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Augustus%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kesselly%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Natalie%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Anosova%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hubert%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lam%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Harry%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kleanthous%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jeremy%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yethon%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Staphylococcus%20epidermidis%20is%20normally%20a%20commensal%20colonizer%20of%20human%20skin%20and%20mucus%20membranes%2C%20but%2C%20due%20to%20its%20ability%20to%20form%20biofilms%20on%20indwelling%20medical%20devices%2C%20it%20has%20emerged%20as%20a%20leading%20cause%20of%20nosocomial%20infections.%20Bacteremia%20or%20bloodstream%20infection%20is%20a%20frequent%20and%20costly%20complication%20resulting%20from%20biofilm%20fouling%20of%20medical%20devices.%20Our%20goal%20was%20to%20develop%20a%20murine%20model%20of%20S.%20epidermidis%20infection%20to%20identify%20potential%20vaccine%20targets%20for%20the%20prevention%20of%20S.%20epidermidis%20bacteremia.%20However%2C%20assessing%20the%20contribution%20of%20adaptive%20immunity%20to%20protection%20against%20S.%20epidermidis%20challenge%20was%20complicated%20by%20a%20highly%20efficacious%20innate%20immune%20response%20in%20mice.%20Naive%20mice%20rapidly%20cleared%20S.%20epidermidis%20infections%20from%20blood%20and%20solid%20organs%2C%20even%20when%20the%20animals%20were%20immunocompromised.%20Cyclophosphamide-mediated%20leukopenia%20reduced%20the%20size%20of%20the%20bacterial%20challenge%20dose%20required%20to%20cause%20lethality%20but%20did%20not%20impair%20clearance%20after%20a%20nonlethal%20challenge.%20Nonspecific%20innate%20immune%20stimulation%2C%20such%20as%20treatment%20with%20a%20Toll-like%20receptor%204%20%28TLR4%29%20agonist%2C%20enhanced%20bacterial%20clearance.%20TLR2%20signaling%20was%20confirmed%20to%20accelerate%20the%20clearance%20of%20S.%20epidermidis%20bacteremia%2C%20but%20TLR2%5Cu2212%5C%2F%5Cu2212%20mice%20could%20still%20resolve%20a%20bloodstream%20infection.%20Furthermore%2C%20TLR2%20signaling%20played%20no%20role%20in%20the%20clearance%20of%20bacteria%20from%20the%20spleen.%20In%20conclusion%2C%20these%20data%20suggest%20that%20S.%20epidermidis%20bloodstream%20infection%20is%20cleared%20in%20a%20highly%20efficient%20manner%20that%20is%20mediated%20by%20both%20TLR2-dependent%20and%20-independent%20innate%20immune%20mechanisms.%20The%20inability%20to%20establish%20a%20persistent%20infection%20in%20mice%2C%20even%20in%20immunocompromised%20animals%2C%20rendered%20these%20murine%20models%20unsuitable%20for%20meaningful%20assessment%20of%20antibody-mediated%20therapies%20or%20vaccine%20candidates.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2204%5C%2F01%5C%2F2016%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1128%5C%2FIAI.01472-15%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220019-9567%2C%201098-5522%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fiai.asm.org%5C%2Fcontent%5C%2F84%5C%2F4%5C%2F1143%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-06-24T16%3A04%3A27Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22WHU2R9PH%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Adamo%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BAdamo%2C%20R.%20F.%2C%20Fishbein%2C%20I.%2C%20Zhang%2C%20K.%2C%20Wen%2C%20J.%2C%20Levy%2C%20R.%20J.%2C%20Alferiev%2C%20I.%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Chorny%2C%20M.%20%282016%29.%20Magnetically%20enhanced%20cell%20delivery%20for%20accelerating%20recovery%20of%20the%20endothelium%20in%20injured%20arteries.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BJournal%20of%20Controlled%20Release%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B222%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20169%26%23x2013%3B175.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jconrel.2015.12.025%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jconrel.2015.12.025%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Magnetically%20enhanced%20cell%20delivery%20for%20accelerating%20recovery%20of%20the%20endothelium%20in%20injured%20arteries%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Adamo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ilia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fishbein%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kehan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Justin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Robert%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Levy%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ivan%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Alferiev%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chorny%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2201%5C%2F2016%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.jconrel.2015.12.025%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2201683659%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0168365915302777%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-31T19%3A10%3A51Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22EUVQTK9R%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Falendysz%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-10-30%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BFalendysz%2C%20E.%20A.%2C%20Lopera%2C%20J.%20G.%2C%20Lorenzsonn%2C%20F.%2C%20Salzer%2C%20J.%20S.%2C%20Hutson%2C%20C.%20L.%2C%20Doty%2C%20J.%2C%20Gallardo-Romero%2C%20N.%2C%20Carroll%2C%20D.%20S.%2C%20Osorio%2C%20J.%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Rocke%2C%20T.%20E.%20%282015%29.%20Further%20Assessment%20of%20Monkeypox%20Virus%20Infection%20in%20Gambian%20Pouched%20Rats%20%28Cricetomys%20gambianus%29%20Using%20In%20Vivo%20Bioluminescent%20Imaging.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLOS%20Neglected%20Tropical%20Diseases%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B9%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2810%29%2C%20e0004130.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pntd.0004130%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pntd.0004130%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Further%20Assessment%20of%20Monkeypox%20Virus%20Infection%20in%20Gambian%20Pouched%20Rats%20%28Cricetomys%20gambianus%29%20Using%20In%20Vivo%20Bioluminescent%20Imaging%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Elizabeth%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Falendysz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Juan%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lopera%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Faye%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lorenzsonn%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Johanna%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Salzer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Christina%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hutson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jeffrey%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Doty%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Nadia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gallardo-Romero%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Darin%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Carroll%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jorge%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Osorio%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tonie%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rocke%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20Desiree%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22LaBeaud%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-10-30%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pntd.0004130%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221935-2735%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pntd.0004130%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-31T20%3A36%3A31Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22AE8Z6UCD%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Rosen%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-09-07%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BRosen%2C%20D.%20A.%2C%20Hilliard%2C%20J.%20K.%2C%20Tiemann%2C%20K.%20M.%2C%20Todd%2C%20E.%20M.%2C%20Morley%2C%20S.%20C.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Hunstad%2C%20D.%20A.%20%282015%29.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BKlebsiella%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3Bpneumoniae%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%20FimK%20Promotes%20Virulence%20in%20Murine%20Pneumonia.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BJournal%20of%20Infectious%20Diseases%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20jiv440.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Finfdis%5C%2Fjiv440%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Finfdis%5C%2Fjiv440%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22%3Ci%3EKlebsiella%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%3Ci%3Epneumoniae%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20FimK%20Promotes%20Virulence%20in%20Murine%20Pneumonia%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rosen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Julia%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hilliard%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kristin%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tiemann%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Elizabeth%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Todd%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20Celeste%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Morley%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hunstad%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-09-07%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Finfdis%5C%2Fjiv440%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220022-1899%2C%201537-6613%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjid.oxfordjournals.org%5C%2Flookup%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Finfdis%5C%2Fjiv440%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T17%3A05%3A32Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22BN2IQT7C%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Liao%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-03-16%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BLiao%2C%20X.%2C%20Ren%2C%20J.%2C%20Wei%2C%20C.-H.%2C%20Ross%2C%20A.%20C.%2C%20Cecere%2C%20T.%20E.%2C%20Jortner%2C%20B.%20S.%2C%20Ahmed%2C%20S.%20A.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Luo%2C%20X.%20M.%20%282015%29.%20Paradoxical%20Effects%20of%20All-Trans-Retinoic%20Acid%20on%20Lupus-Like%20Disease%20in%20the%20MRL%5C%2Flpr%20Mouse%20Model.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLOS%20ONE%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B10%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%283%29%2C%20e0118176.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0118176%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0118176%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Paradoxical%20Effects%20of%20All-Trans-Retinoic%20Acid%20on%20Lupus-Like%20Disease%20in%20the%20MRL%5C%2Flpr%20Mouse%20Model%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Xiaofeng%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Liao%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jingjing%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ren%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Cheng-Hsin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wei%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20Catharine%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ross%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Thomas%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cecere%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bernard%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Jortner%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20Ansar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ahmed%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Xin%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Luo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Colette%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kanellopoulos-Langevin%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-3-16%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0118176%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0118176%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-10-30T20%3A24%3A51Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%2286R5RVKZ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Caverly%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-02-12%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BCaverly%2C%20L.%20J.%2C%20Caceres%2C%20S.%20M.%2C%20Fratelli%2C%20C.%2C%20Happoldt%2C%20C.%2C%20Kidwell%2C%20K.%20M.%2C%20Malcolm%2C%20K.%20C.%2C%20Nick%2C%20J.%20A.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Nichols%2C%20D.%20P.%20%282015%29.%20Mycobacterium%20abscessus%20Morphotype%20Comparison%20in%20a%20Murine%20Model.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLOS%20ONE%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B10%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%282%29%2C%20e0117657.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0117657%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0117657%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Mycobacterium%20abscessus%20Morphotype%20Comparison%20in%20a%20Murine%20Model%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lindsay%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Caverly%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Silvia%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Caceres%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Cori%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fratelli%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Carrie%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Happoldt%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kelley%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kidwell%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kenneth%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Malcolm%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jerry%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nick%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nichols%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Nades%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Palaniyar%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-2-12%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0117657%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0117657%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-06-19T19%3A41%3A01Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%229544DNCZ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Palomares%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPalomares%2C%20R.%20A.%2C%20Sakamoto%2C%20K.%2C%20Walz%2C%20H.%20L.%2C%20Brock%2C%20K.%20V.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Hurley%2C%20D.%20J.%20%282015%29.%20Acute%20infection%20with%20bovine%20viral%20diarrhea%20virus%20of%20low%20or%20high%20virulence%20leads%20to%20depletion%20and%20redistribution%20of%20WC1%2B%20%26%23x3B3%3B%26%23x3B4%3B%20T%20cells%20in%20lymphoid%20tissues%20of%20beef%20calves.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BVeterinary%20Immunology%20and%20Immunopathology%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B167%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%283%26%23x2013%3B4%29%2C%20190%26%23x2013%3B195.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.vetimm.2015.07.016%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.vetimm.2015.07.016%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Acute%20infection%20with%20bovine%20viral%20diarrhea%20virus%20of%20low%20or%20high%20virulence%20leads%20to%20depletion%20and%20redistribution%20of%20WC1%2B%20%5Cu03b3%5Cu03b4%20T%20cells%20in%20lymphoid%20tissues%20of%20beef%20calves%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Roberto%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Palomares%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kaori%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sakamoto%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Heather%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Walz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kenny%20V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Brock%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hurley%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2210%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.vetimm.2015.07.016%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2201652427%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0165242715001737%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T18%3A30%3A23Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%222IEVS26G%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Neishabouri%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BNeishabouri%2C%20S.%20H.%2C%20Hutson%2C%20S.%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Davoodi%2C%20J.%20%282015%29.%20Chronic%20activation%20of%20mTOR%20complex%201%20by%20branched%20chain%20amino%20acids%20and%20organ%20hypertrophy.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BAmino%20Acids%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B47%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%286%29%2C%201167%26%23x2013%3B1182.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs00726-015-1944-y%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs00726-015-1944-y%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Chronic%20activation%20of%20mTOR%20complex%201%20by%20branched%20chain%20amino%20acids%20and%20organ%20hypertrophy%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20Hallaj%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Neishabouri%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hutson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Davoodi%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%226%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1007%5C%2Fs00726-015-1944-y%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220939-4451%2C%201438-2199%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs00726-015-1944-y%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-31T16%3A24%3A29Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22TGMMS3AV%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Lopera%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BLopera%2C%20J.%20G.%2C%20Falendysz%2C%20E.%20A.%2C%20Rocke%2C%20T.%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Osorio%2C%20J.%20E.%20%282015%29.%20Attenuation%20of%20monkeypox%20virus%20by%20deletion%20of%20genomic%20regions.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BVirology%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B475%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20129%26%23x2013%3B138.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.virol.2014.11.009%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.virol.2014.11.009%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Attenuation%20of%20monkeypox%20virus%20by%20deletion%20of%20genomic%20regions%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Juan%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lopera%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Elizabeth%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Falendysz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tonie%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rocke%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jorge%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Osorio%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2201%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.virol.2014.11.009%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2200426822%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0042682214005030%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-31T21%3A52%3A28Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22VUMRWEAW%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Eriksson%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BEriksson%2C%20A.%2C%20Williams%2C%20M.%20J.%2C%20Voisin%2C%20S.%2C%20Hansson%2C%20I.%2C%20Krishnan%2C%20A.%2C%20Philippot%2C%20G.%2C%20Yamskova%2C%20O.%2C%20Herisson%2C%20F.%20M.%2C%20Dnyansagar%2C%20R.%2C%20Moschonis%2C%20G.%2C%20Manios%2C%20Y.%2C%20Chrousos%2C%20G.%20P.%2C%20Olszewski%2C%20P.%20K.%2C%20Frediksson%2C%20R.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Schi%26%23xF6%3Bth%2C%20H.%20B.%20%282015%29.%20Implication%20of%20coronin%207%20in%20body%20weight%20regulation%20in%20humans%2C%20mice%20and%20flies.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BBMC%20Neuroscience%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B16%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%281%29%2C%2013.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0151-9%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0151-9%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Implication%20of%20coronin%207%20in%20body%20weight%20regulation%20in%20humans%2C%20mice%20and%20flies%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anders%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Eriksson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%20J%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Williams%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sarah%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Voisin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ida%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hansson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Arunkumar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Krishnan%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Gaetan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Philippot%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Olga%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yamskova%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Florence%20M%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Herisson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rohit%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dnyansagar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22George%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Moschonis%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yannis%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Manios%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22George%20P%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chrousos%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Pawel%20K%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Olszewski%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Robert%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Frediksson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Helgi%20B%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schi%5Cu00f6th%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0151-9%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221471-2202%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomedcentral.com%5C%2F1471-2202%5C%2F16%5C%2F13%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-31T20%3A09%3A52Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%227EWWE2E8%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Zhang%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BZhang%2C%20Z.%2C%20He%2C%20L.%2C%20Hu%2C%20S.%2C%20Wang%2C%20Y.%2C%20Lai%2C%20Q.%2C%20Yang%2C%20P.%2C%20Yu%2C%20Q.%2C%20Zhang%2C%20S.%2C%20Xiong%2C%20F.%2C%20Simsekyilmaz%2C%20S.%2C%20Ning%2C%20Q.%2C%20Li%2C%20J.%2C%20Zhang%2C%20D.%2C%20Zhang%2C%20H.%2C%20Xiang%2C%20X.%2C%20Zhou%2C%20Z.%2C%20Sun%2C%20H.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Wang%2C%20C.-Y.%20%282015%29.%20AAL%20exacerbates%20pro-inflammatory%20response%20in%20macrophages%20by%20regulating%20Mincle%5C%2FSyk%5C%2FCard9%20signaling%20along%20with%20the%20Nlrp3%20inflammasome%20assembly.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BAmerican%20Journal%20of%20Translational%20Research%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B7%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2810%29%2C%201812%26%23x2013%3B1825.%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22AAL%20exacerbates%20pro-inflammatory%20response%20in%20macrophages%20by%20regulating%20Mincle%5C%2FSyk%5C%2FCard9%20signaling%20along%20with%20the%20Nlrp3%20inflammasome%20assembly%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Zhijun%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Long%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22He%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shuang%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yi%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Qiaohong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lai%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ping%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Qilin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shu%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Fei%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Xiong%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sakine%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Simsekyilmaz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Qin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ning%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jinxiu%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Li%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dongshan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hongliang%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Xudong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Xiang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Zhiguang%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhou%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hui%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sun%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Cong-Yi%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wang%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%22%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T20%3A03%3A39Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22JFW4Q8B3%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Hyatt%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-10-09%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BHyatt%2C%20L.%20D.%2C%20Wasserman%2C%20G.%20A.%2C%20Rah%2C%20Y.%20J.%2C%20Matsuura%2C%20K.%20Y.%2C%20Coleman%2C%20F.%20T.%2C%20Hilliard%2C%20K.%20L.%2C%20Pepper-Cunningham%2C%20Z.%20A.%2C%20Ieong%2C%20M.%2C%20Stumpo%2C%20D.%20J.%2C%20Blackshear%2C%20P.%20J.%2C%20Quinton%2C%20L.%20J.%2C%20Mizgerd%2C%20J.%20P.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Jones%2C%20M.%20R.%20%282014%29.%20Myeloid%20ZFP36L1%20Does%20Not%20Regulate%20Inflammation%20or%20Host%20Defense%20in%20Mouse%20Models%20of%20Acute%20Bacterial%20Infection.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLoS%20ONE%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B9%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2810%29%2C%20e109072.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0109072%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0109072%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Myeloid%20ZFP36L1%20Does%20Not%20Regulate%20Inflammation%20or%20Host%20Defense%20in%20Mouse%20Models%20of%20Acute%20Bacterial%20Infection%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lynnae%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hyatt%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Gregory%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wasserman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yoon%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rah%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kori%20Y.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Matsuura%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Fadie%20T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Coleman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kristie%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hilliard%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Zachary%20Ash%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pepper-Cunningham%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ieong%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Deborah%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Stumpo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Perry%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Blackshear%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lee%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Quinton%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Joseph%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mizgerd%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Matthew%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Jones%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bernhard%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ryffel%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014-10-9%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0109072%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0109072%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-31T17%3A48%3A01Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22Q4JUKZIR%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Bannantine%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-07-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BBannantine%2C%20J.%20P.%2C%20Everman%2C%20J.%20L.%2C%20Rose%2C%20S.%20J.%2C%20Babrak%2C%20L.%2C%20Katani%2C%20R.%2C%20Barletta%2C%20R.%20G.%2C%20Talaat%2C%20A.%20M.%2C%20Grohn%2C%20Y.%20T.%2C%20Chang%2C%20Y.-F.%2C%20Kapur%2C%20V.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Bermudez%2C%20L.%20E.%20%282014%29.%20Evaluation%20of%20eight%20live%20attenuated%20vaccine%20candidates%20for%20protection%20against%20challenge%20with%20virulent%20Mycobacterium%20avium%20subspecies%20paratuberculosis%20in%20mice.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BFrontiers%20in%20Cellular%20and%20Infection%20Microbiology%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B4%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffcimb.2014.00088%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffcimb.2014.00088%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Evaluation%20of%20eight%20live%20attenuated%20vaccine%20candidates%20for%20protection%20against%20challenge%20with%20virulent%20Mycobacterium%20avium%20subspecies%20paratuberculosis%20in%20mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22John%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bannantine%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jamie%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Everman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sasha%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rose%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lmar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Babrak%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Robab%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Katani%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Raul%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Barletta%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Adel%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Talaat%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yrjo%20T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Grohn%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yung-Fu%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Vivek%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kapur%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Luiz%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bermudez%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014-07-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3389%5C%2Ffcimb.2014.00088%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222235-2988%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjournal.frontiersin.org%5C%2Farticle%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffcimb.2014.00088%5C%2Fabstract%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-12T18%3A53%3A29Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%228VX9CN6V%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Palomares%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPalomares%2C%20R.%20A.%2C%20Hurley%2C%20D.%20J.%2C%20Woolums%2C%20A.%20R.%2C%20Parrish%2C%20J.%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Brock%2C%20K.%20V.%20%282014%29.%20Analysis%20of%20mRNA%20expression%20for%20genes%20associated%20with%20regulatory%20T%20lymphocytes%20%28CD25%2C%20FoxP3%2C%20CTLA4%2C%20and%20IDO%29%20after%20experimental%20infection%20with%20bovine%20viral%20diarrhea%20virus%20of%20low%20or%20high%20virulence%20in%20beef%20calves.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BComparative%20Immunology%2C%20Microbiology%20and%20Infectious%20Diseases%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B37%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%285%26%23x2013%3B6%29%2C%20331%26%23x2013%3B338.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.cimid.2014.10.001%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.cimid.2014.10.001%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Analysis%20of%20mRNA%20expression%20for%20genes%20associated%20with%20regulatory%20T%20lymphocytes%20%28CD25%2C%20FoxP3%2C%20CTLA4%2C%20and%20IDO%29%20after%20experimental%20infection%20with%20bovine%20viral%20diarrhea%20virus%20of%20low%20or%20high%20virulence%20in%20beef%20calves%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Roberto%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Palomares%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hurley%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Amelia%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Woolums%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jacqueline%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Parrish%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kenny%20V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Brock%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.cimid.2014.10.001%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2201479571%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0147957114000538%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-13T21%3A53%3A00Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22QDX23HZG%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Palomares%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPalomares%2C%20R.%20A.%2C%20Parrish%2C%20J.%2C%20Woolums%2C%20A.%20R.%2C%20Brock%2C%20K.%20V.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Hurley%2C%20D.%20J.%20%282014%29.%20Expression%20of%20toll-like%20receptors%20and%20co-stimulatory%20molecules%20in%20lymphoid%20tissue%20during%20experimental%20infection%20of%20beef%20calves%20with%20bovine%20viral%20diarrhea%20virus%20of%20low%20and%20high%20virulence.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BVeterinary%20Research%20Communications%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B38%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%284%29%2C%20329%26%23x2013%3B335.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs11259-014-9613-2%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs11259-014-9613-2%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Expression%20of%20toll-like%20receptors%20and%20co-stimulatory%20molecules%20in%20lymphoid%20tissue%20during%20experimental%20infection%20of%20beef%20calves%20with%20bovine%20viral%20diarrhea%20virus%20of%20low%20and%20high%20virulence%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Roberto%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Palomares%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jacqueline%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Parrish%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Amelia%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Woolums%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kenny%20V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Brock%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hurley%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1007%5C%2Fs11259-014-9613-2%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220165-7380%2C%201573-7446%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs11259-014-9613-2%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-19T14%3A23%3A55Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22X9F9E8BR%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Borschensky%20and%20Reinacher%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BBorschensky%2C%20C.%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Reinacher%2C%20M.%20%282014%29.%20Mutations%20in%20the%203c%20and%207b%20genes%20of%20feline%20coronavirus%20in%20spontaneously%20affected%20FIP%20cats.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BResearch%20in%20Veterinary%20Science%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B97%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%282%29%2C%20333%26%23x2013%3B340.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.rvsc.2014.07.016%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.rvsc.2014.07.016%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Mutations%20in%20the%203c%20and%207b%20genes%20of%20feline%20coronavirus%20in%20spontaneously%20affected%20FIP%20cats%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Borschensky%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Reinacher%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2210%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.rvsc.2014.07.016%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2200345288%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0034528814002185%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-10-30T19%3A39%3A51Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22338HHQRM%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Palomares%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPalomares%2C%20R.%20A.%2C%20Brock%2C%20K.%20V.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Walz%2C%20P.%20H.%20%282014%29.%20Differential%20expression%20of%20pro-inflammatory%20and%20anti-inflammatory%20cytokines%20during%20experimental%20infection%20with%20low%20or%20high%20virulence%20bovine%20viral%20diarrhea%20virus%20in%20beef%20calves.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BVeterinary%20Immunology%20and%20Immunopathology%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B157%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%283%26%23x2013%3B4%29%2C%20149%26%23x2013%3B154.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.vetimm.2013.12.002%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.vetimm.2013.12.002%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Differential%20expression%20of%20pro-inflammatory%20and%20anti-inflammatory%20cytokines%20during%20experimental%20infection%20with%20low%20or%20high%20virulence%20bovine%20viral%20diarrhea%20virus%20in%20beef%20calves%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Roberto%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Palomares%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kenny%20V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Brock%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Paul%20H.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Walz%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2202%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.vetimm.2013.12.002%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2201652427%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0165242713003176%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-12T16%3A42%3A17Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22CG63U65K%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Melero%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BMelero%2C%20M.%2C%20Garc%26%23xED%3Ba-P%26%23xE1%3Brraga%2C%20D.%2C%20Corpa%2C%20J.%2C%20Ortega%2C%20J.%2C%20Rubio-Guerri%2C%20C.%2C%20Crespo%2C%20J.%2C%20Rivera-Arroyo%2C%20B.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20S%26%23xE1%3Bnchez-Vizca%26%23xED%3Bno%2C%20J.%20%282014%29.%20First%20molecular%20detection%20and%20characterization%20of%20herpesvirus%20and%20poxvirus%20in%20a%20Pacific%20walrus%20%28Odobenus%20rosmarus%20divergens%29.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BBMC%20Veterinary%20Research%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B10%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%281%29%2C%20968.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12917-014-0308-2%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12917-014-0308-2%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22First%20molecular%20detection%20and%20characterization%20of%20herpesvirus%20and%20poxvirus%20in%20a%20Pacific%20walrus%20%28Odobenus%20rosmarus%20divergens%29%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Melero%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Daniel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Garc%5Cu00eda-P%5Cu00e1rraga%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Juan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Corpa%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Joaqu%5Cu00edn%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ortega%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Consuelo%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rubio-Guerri%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jos%5Cu00e9%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Crespo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bel%5Cu00e9n%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rivera-Arroyo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jos%5Cu00e9%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22S%5Cu00e1nchez-Vizca%5Cu00edno%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1186%5C%2Fs12917-014-0308-2%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221746-6148%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomedcentral.com%5C%2F1746-6148%5C%2F10%5C%2F968%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-12T17%3A25%3A07Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22N9BNIMJV%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Erickson%20and%20Pfeiffer%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-11-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BErickson%2C%20A.%20K.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Pfeiffer%2C%20J.%20K.%20%282013%29.%20Dynamic%20Viral%20Dissemination%20in%20Mice%20Infected%20with%20Yellow%20Fever%20Virus%20Strain%2017D.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BJournal%20of%20Virology%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B87%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2822%29%2C%2012392%26%23x2013%3B12397.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1128%5C%2FJVI.02149-13%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1128%5C%2FJVI.02149-13%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Dynamic%20Viral%20Dissemination%20in%20Mice%20Infected%20with%20Yellow%20Fever%20Virus%20Strain%2017D%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Erickson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pfeiffer%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-11-15%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1128%5C%2FJVI.02149-13%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220022-538X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjvi.asm.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1128%5C%2FJVI.02149-13%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T16%3A31%3A52Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22SX6DRESC%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Wiles%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-08-22%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BWiles%2C%20T.%20J.%2C%20Norton%2C%20J.%20P.%2C%20Russell%2C%20C.%20W.%2C%20Dalley%2C%20B.%20K.%2C%20Fischer%2C%20K.%20F.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Mulvey%2C%20M.%20A.%20%282013%29.%20Combining%20Quantitative%20Genetic%20Footprinting%20and%20Trait%20Enrichment%20Analysis%20to%20Identify%20Fitness%20Determinants%20of%20a%20Bacterial%20Pathogen.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLoS%20Genetics%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B9%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%288%29%2C%20e1003716.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pgen.1003716%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pgen.1003716%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Combining%20Quantitative%20Genetic%20Footprinting%20and%20Trait%20Enrichment%20Analysis%20to%20Identify%20Fitness%20Determinants%20of%20a%20Bacterial%20Pathogen%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Travis%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wiles%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20Paul%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Norton%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Colin%20W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Russell%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Brian%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dalley%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kael%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fischer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Matthew%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mulvey%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Danielle%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Garsin%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-8-22%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pgen.1003716%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221553-7404%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pgen.1003716%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-22T14%3A40%3A33Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22GKPPUJBR%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Silver%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-08-05%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BSilver%2C%20A.%20C.%2C%20Dunne%2C%20D.%20W.%2C%20Zeiss%2C%20C.%20J.%2C%20Bockenstedt%2C%20L.%20K.%2C%20Radolf%2C%20J.%20D.%2C%20Salazar%2C%20J.%20C.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Fikrig%2C%20E.%20%282013%29.%20MyD88%20Deficiency%20Markedly%20Worsens%20Tissue%20Inflammation%20and%20Bacterial%20Clearance%20in%20Mice%20Infected%20with%20Treponema%20pallidum%2C%20the%20Agent%20of%20Syphilis.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLoS%20ONE%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B8%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%288%29%2C%20e71388.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0071388%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0071388%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22MyD88%20Deficiency%20Markedly%20Worsens%20Tissue%20Inflammation%20and%20Bacterial%20Clearance%20in%20Mice%20Infected%20with%20Treponema%20pallidum%2C%20the%20Agent%20of%20Syphilis%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Adam%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Silver%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dana%20W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dunne%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Caroline%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zeiss%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Linda%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bockenstedt%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Justin%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Radolf%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Juan%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Salazar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Erol%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fikrig%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Adam%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ratner%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-8-5%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0071388%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0071388%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-22T14%3A23%3A10Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22ISH32D5C%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Karauzum%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-06-07%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BKarauzum%2C%20H.%2C%20Adhikari%2C%20R.%20P.%2C%20Sarwar%2C%20J.%2C%20Devi%2C%20V.%20S.%2C%20Abaandou%2C%20L.%2C%20Haudenschild%2C%20C.%2C%20Mahmoudieh%2C%20M.%2C%20Boroun%2C%20A.%20R.%2C%20Vu%2C%20H.%2C%20Nguyen%2C%20T.%2C%20Warfield%2C%20K.%20L.%2C%20Shulenin%2C%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Aman%2C%20M.%20J.%20%282013%29.%20Structurally%20Designed%20Attenuated%20Subunit%20Vaccines%20for%20S.%20aureus%20LukS-PV%20and%20LukF-PV%20Confer%20Protection%20in%20a%20Mouse%20Bacteremia%20Model.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLoS%20ONE%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B8%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%286%29%2C%20e65384.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065384%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065384%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Structurally%20Designed%20Attenuated%20Subunit%20Vaccines%20for%20S.%20aureus%20LukS-PV%20and%20LukF-PV%20Confer%20Protection%20in%20a%20Mouse%20Bacteremia%20Model%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hatice%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Karauzum%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rajan%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Adhikari%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jawad%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sarwar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22V.%20Sathya%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Devi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Laura%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Abaandou%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Christian%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Haudenschild%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mahta%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mahmoudieh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Atefeh%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Boroun%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tam%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nguyen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kelly%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Warfield%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sergey%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Shulenin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20Javad%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Aman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dipshikha%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chakravortty%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-6-7%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065384%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065384%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T17%3A21%3A51Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22UDX5RMR7%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Chorny%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-06-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BChorny%2C%20M.%2C%20Fishbein%2C%20I.%2C%20Tengood%2C%20J.%20E.%2C%20Adamo%2C%20R.%20F.%2C%20Alferiev%2C%20I.%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Levy%2C%20R.%20J.%20%282013%29.%20Site-specific%20gene%20delivery%20to%20stented%20arteries%20using%20magnetically%20guided%20zinc%20oleate-based%20nanoparticles%20loaded%20with%20adenoviral%20vectors.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BThe%20FASEB%20Journal%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B27%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%286%29%2C%202198%26%23x2013%3B2206.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1096%5C%2Ffj.12-224659%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1096%5C%2Ffj.12-224659%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Site-specific%20gene%20delivery%20to%20stented%20arteries%20using%20magnetically%20guided%20zinc%20oleate-based%20nanoparticles%20loaded%20with%20adenoviral%20vectors%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chorny%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22I.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fishbein%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tengood%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Adamo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22I.%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Alferiev%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Levy%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-06-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1096%5C%2Ffj.12-224659%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220892-6638%2C%201530-6860%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.fasebj.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1096%5C%2Ffj.12-224659%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-23T14%3A51%3A38Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22XZNXAQDX%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Nichols%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BNichols%2C%20D.%20P.%2C%20Caceres%2C%20S.%2C%20Caverly%2C%20L.%2C%20Fratelli%2C%20C.%2C%20Kim%2C%20S.%20H.%2C%20Malcolm%2C%20K.%2C%20Poch%2C%20K.%20R.%2C%20Saavedra%2C%20M.%2C%20Solomon%2C%20G.%2C%20Taylor-Cousar%2C%20J.%2C%20Moskowitz%2C%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Nick%2C%20J.%20A.%20%282013%29.%20Effects%20of%20azithromycin%20in%20Pseudomonas%20aeruginosa%20burn%20wound%20infection.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BJournal%20of%20Surgical%20Research%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B183%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%282%29%2C%20767%26%23x2013%3B776.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jss.2013.02.003%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jss.2013.02.003%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Effects%20of%20azithromycin%20in%20Pseudomonas%20aeruginosa%20burn%20wound%20infection%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nichols%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Silvia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Caceres%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lindsay%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Caverly%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Cori%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fratelli%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sun%20Ho%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kim%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ken%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Malcolm%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Katie%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Poch%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Milene%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Saavedra%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22George%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Solomon%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jennifer%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Taylor-Cousar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Samuel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Moskowitz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jerry%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nick%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%228%5C%2F2013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.jss.2013.02.003%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2200224804%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0022480413000887%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-22T13%3A56%3A00Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%228ETQ38JW%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Palomares%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPalomares%2C%20R.%20A.%2C%20Walz%2C%20H.%20G.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Brock%2C%20K.%20V.%20%282013%29.%20Expression%20of%20type%20I%20interferon-induced%20antiviral%20state%20and%20pro-apoptosis%20markers%20during%20experimental%20infection%20with%20low%20or%20high%20virulence%20bovine%20viral%20diarrhea%20virus%20in%20beef%20calves.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BVirus%20Research%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B173%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%282%29%2C%20260%26%23x2013%3B269.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.virusres.2013.02.010%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.virusres.2013.02.010%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Expression%20of%20type%20I%20interferon-induced%20antiviral%20state%20and%20pro-apoptosis%20markers%20during%20experimental%20infection%20with%20low%20or%20high%20virulence%20bovine%20viral%20diarrhea%20virus%20in%20beef%20calves%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Roberto%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Palomares%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Heather%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Walz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kenny%20V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Brock%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%225%5C%2F2013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.virusres.2013.02.010%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2201681702%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0168170213000609%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-13T14%3A41%3A28Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22PQZN3538%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Poulsen%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPoulsen%2C%20K.%20P.%2C%20Faith%2C%20N.%20G.%2C%20Steinberg%2C%20H.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Czuprynski%2C%20C.%20J.%20%282013%29.%20Bacterial%20load%20and%20inflammation%20in%20fetal%20tissues%20is%20not%20dependent%20on%20IL-17a%20or%20IL-22%20in%2010%26%23x2013%3B14%20day%20pregnant%20mice%20infected%20with%20Listeria%20monocytogenes.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BMicrobial%20Pathogenesis%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B56%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%2047%26%23x2013%3B52.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.micpath.2012.11.003%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.micpath.2012.11.003%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Bacterial%20load%20and%20inflammation%20in%20fetal%20tissues%20is%20not%20dependent%20on%20IL-17a%20or%20IL-22%20in%2010%5Cu201314%20day%20pregnant%20mice%20infected%20with%20Listeria%20monocytogenes%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Keith%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Poulsen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Nancy%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Faith%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Howard%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Steinberg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Charles%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Czuprynski%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%223%5C%2F2013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.micpath.2012.11.003%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2208824010%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0882401012001957%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-22T14%3A05%3A51Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22UV3JU2QE%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Hanstein%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BHanstein%2C%20R.%2C%20Negoro%2C%20H.%2C%20Patel%2C%20N.%20K.%2C%20Charollais%2C%20A.%2C%20Meda%2C%20P.%2C%20Spray%2C%20D.%20C.%2C%20Suadicani%2C%20S.%20O.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Scemes%2C%20E.%20%282013%29.%20Promises%20and%20pitfalls%20of%20a%20Pannexin1%20transgenic%20mouse%20line.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BFrontiers%20in%20Pharmacology%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B4%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphar.2013.00061%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphar.2013.00061%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Promises%20and%20pitfalls%20of%20a%20Pannexin1%20transgenic%20mouse%20line%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Regina%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hanstein%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hiromitsu%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Negoro%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Naman%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Patel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anne%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Charollais%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Paolo%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Meda%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spray%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sylvia%20O.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Suadicani%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eliana%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Scemes%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3389%5C%2Ffphar.2013.00061%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221663-9812%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjournal.frontiersin.org%5C%2Farticle%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphar.2013.00061%5C%2Fabstract%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T17%3A15%3A36Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22Q8DJCEEE%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Austin%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012-11-19%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BAustin%2C%20W.%20R.%2C%20Armijo%2C%20A.%20L.%2C%20Campbell%2C%20D.%20O.%2C%20Singh%2C%20A.%20S.%2C%20Hsieh%2C%20T.%2C%20Nathanson%2C%20D.%2C%20Herschman%2C%20H.%20R.%2C%20Phelps%2C%20M.%20E.%2C%20Witte%2C%20O.%20N.%2C%20Czernin%2C%20J.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Radu%2C%20C.%20G.%20%282012%29.%20Nucleoside%20salvage%20pathway%20kinases%20regulate%20hematopoiesis%20by%20linking%20nucleotide%20metabolism%20with%20replication%20stress.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BJournal%20of%20Experimental%20Medicine%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B209%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2812%29%2C%202215%26%23x2013%3B2228.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1084%5C%2Fjem.20121061%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1084%5C%2Fjem.20121061%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Nucleoside%20salvage%20pathway%20kinases%20regulate%20hematopoiesis%20by%20linking%20nucleotide%20metabolism%20with%20replication%20stress%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22W.%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Austin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Armijo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%20O.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Campbell%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Singh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hsieh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nathanson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22H.%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Herschman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Phelps%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22O.%20N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Witte%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Czernin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Radu%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222012-11-19%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1084%5C%2Fjem.20121061%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220022-1007%2C%201540-9538%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.jem.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1084%5C%2Fjem.20121061%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T15%3A33%3A32Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22GUA4RTZR%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Kumar%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012-08-31%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BKumar%2C%20M.%2C%20Roe%2C%20K.%2C%20Nerurkar%2C%20P.%20V.%2C%20Namekar%2C%20M.%2C%20Orillo%2C%20B.%2C%20Verma%2C%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Nerurkar%2C%20V.%20R.%20%282012%29.%20Impaired%20Virus%20Clearance%2C%20Compromised%20Immune%20Response%20and%20Increased%20Mortality%20in%20Type%202%20Diabetic%20Mice%20Infected%20with%20West%20Nile%20Virus.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLoS%20ONE%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B7%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%288%29%2C%20e44682.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0044682%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0044682%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Impaired%20Virus%20Clearance%2C%20Compromised%20Immune%20Response%20and%20Increased%20Mortality%20in%20Type%202%20Diabetic%20Mice%20Infected%20with%20West%20Nile%20Virus%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mukesh%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kumar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kelsey%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Roe%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Pratibha%20V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nerurkar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Madhuri%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Namekar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Beverly%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Orillo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Saguna%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Verma%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Vivek%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nerurkar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Robyn%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Klein%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222012-8-31%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0044682%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0044682%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T17%3A23%3A53Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22ZPMRDRZ2%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Adhikari%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012-06-06%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BAdhikari%2C%20R.%20P.%2C%20Karauzum%2C%20H.%2C%20Sarwar%2C%20J.%2C%20Abaandou%2C%20L.%2C%20Mahmoudieh%2C%20M.%2C%20Boroun%2C%20A.%20R.%2C%20Vu%2C%20H.%2C%20Nguyen%2C%20T.%2C%20Devi%2C%20V.%20S.%2C%20Shulenin%2C%20S.%2C%20Warfield%2C%20K.%20L.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Aman%2C%20M.%20J.%20%282012%29.%20Novel%20Structurally%20Designed%20Vaccine%20for%20S.%20aureus%20%26%23x3B1%3B-Hemolysin%3A%20Protection%20against%20Bacteremia%20and%20Pneumonia.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLoS%20ONE%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B7%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%286%29%2C%20e38567.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0038567%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0038567%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Novel%20Structurally%20Designed%20Vaccine%20for%20S.%20aureus%20%5Cu03b1-Hemolysin%3A%20Protection%20against%20Bacteremia%20and%20Pneumonia%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rajan%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Adhikari%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hatice%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Karauzum%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jawad%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sarwar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Laura%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Abaandou%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mahta%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mahmoudieh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Atefeh%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Boroun%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tam%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nguyen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22V.%20Sathya%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Devi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sergey%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Shulenin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kelly%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Warfield%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20Javad%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Aman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Otto%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222012-6-6%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0038567%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0038567%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T15%3A31%3A56Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22HKG38JK4%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Bessen%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222011-12-12%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BBessen%2C%20R.%20A.%2C%20Robinson%2C%20C.%20J.%2C%20Seelig%2C%20D.%20M.%2C%20Watschke%2C%20C.%20P.%2C%20Lowe%2C%20D.%2C%20Shearin%2C%20H.%2C%20Martinka%2C%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Babcock%2C%20A.%20M.%20%282011%29.%20Transmission%20of%20Chronic%20Wasting%20Disease%20Identifies%20a%20Prion%20Strain%20Causing%20Cachexia%20and%20Heart%20Infection%20in%20Hamsters.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLoS%20ONE%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B6%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2812%29%2C%20e28026.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0028026%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0028026%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Transmission%20of%20Chronic%20Wasting%20Disease%20Identifies%20a%20Prion%20Strain%20Causing%20Cachexia%20and%20Heart%20Infection%20in%20Hamsters%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bessen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Cameron%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Robinson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Davis%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Seelig%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Christopher%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Watschke%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Diana%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lowe%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Harold%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Shearin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Scott%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Martinka%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alex%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Babcock%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andrew%20Francis%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hill%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222011-12-12%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0028026%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0028026%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-23T15%3A29%3A19Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22SPAMBSRT%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Smith%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222011-10-27%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BSmith%2C%20J.%20S.%2C%20Xu%2C%20Z.%2C%20Tian%2C%20J.%2C%20Palmer%2C%20D.%20J.%2C%20Ng%2C%20P.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Byrnes%2C%20A.%20P.%20%282011%29.%20The%20Role%20of%20Endosomal%20Escape%20and%20Mitogen-Activated%20Protein%20Kinases%20in%20Adenoviral%20Activation%20of%20the%20Innate%20Immune%20Response.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLoS%20ONE%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B6%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2810%29%2C%20e26755.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0026755%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0026755%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22The%20Role%20of%20Endosomal%20Escape%20and%20Mitogen-Activated%20Protein%20Kinases%20in%20Adenoviral%20Activation%20of%20the%20Innate%20Immune%20Response%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jeffrey%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Smith%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Zhili%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Xu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jie%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tian%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Donna%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Palmer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Philip%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ng%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andrew%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Byrnes%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bernhard%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ryffel%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222011-10-27%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0026755%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0026755%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-23T17%3A54%3A44Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22BFGKQMZA%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Gogal%2C%20Jr.%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222011-02-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BGogal%2C%20Jr.%2C%20R.%20M.%2C%20Kerr%2C%20R.%2C%20Kingsley%2C%20D.%20H.%2C%20Granata%2C%20L.%20A.%2C%20LeRoith%2C%20T.%2C%20Holliman%2C%20S.%20D.%2C%20Dancho%2C%20B.%20A.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Flick%2C%20Jr.%2C%20G.%20J.%20%282011%29.%20High%20Hydrostatic%20Pressure%20Processing%20of%20Murine%20Norovirus%201%26%23x2013%3BContaminated%20Oysters%20Inhibits%20Oral%20Infection%20in%20STAT-1%26amp%3Blt%3BSUP%26amp%3Bgt%3B-%5C%2F-%26amp%3Blt%3B%5C%2FSUP%26amp%3Bgt%3B%26%23x2013%3BDeficient%20Female%20Mice.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BJournal%20of%20Food%20Protection%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B74%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%282%29%2C%20209%26%23x2013%3B214.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.4315%5C%2F0362-028X.JFP-10-235%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.4315%5C%2F0362-028X.JFP-10-235%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22High%20Hydrostatic%20Pressure%20Processing%20of%20Murine%20Norovirus%201%5Cu2013Contaminated%20Oysters%20Inhibits%20Oral%20Infection%20in%20STAT-1%26lt%3BSUP%26gt%3B-%5C%2F-%26lt%3B%5C%2FSUP%26gt%3B%5Cu2013Deficient%20Female%20Mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gogal%2C%20Jr.%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kerr%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%20H.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kingsley%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22L.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Granata%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22LeRoith%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Holliman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dancho%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22G.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Flick%2C%20Jr.%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222011-02-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.4315%5C%2F0362-028X.JFP-10-235%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220362028X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fopenurl.ingenta.com%5C%2Fcontent%5C%2Fxref%3Fgenre%3Darticle%26issn%3D0362-028X%26volume%3D74%26issue%3D2%26spage%3D209%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T16%3A39%3A02Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22EVHFA7JI%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Rayner%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222010-06-18%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BRayner%2C%20K.%20J.%2C%20Suarez%2C%20Y.%2C%20Davalos%2C%20A.%2C%20Parathath%2C%20S.%2C%20Fitzgerald%2C%20M.%20L.%2C%20Tamehiro%2C%20N.%2C%20Fisher%2C%20E.%20A.%2C%20Moore%2C%20K.%20J.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Fernandez-Hernando%2C%20C.%20%282010%29.%20MiR-33%20Contributes%20to%20the%20Regulation%20of%20Cholesterol%20Homeostasis.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BScience%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B328%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%285985%29%2C%201570%26%23x2013%3B1573.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1126%5C%2Fscience.1189862%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1126%5C%2Fscience.1189862%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22MiR-33%20Contributes%20to%20the%20Regulation%20of%20Cholesterol%20Homeostasis%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rayner%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Y.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Suarez%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Davalos%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Parathath%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fitzgerald%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tamehiro%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fisher%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Moore%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fernandez-Hernando%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222010-06-18%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1126%5C%2Fscience.1189862%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220036-8075%2C%201095-9203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencemag.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1126%5C%2Fscience.1189862%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-27T14%3A34%3A20Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%228ADCJV4D%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Lancaster%20and%20Pfeiffer%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222010-03-05%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BLancaster%2C%20K.%20Z.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Pfeiffer%2C%20J.%20K.%20%282010%29.%20Limited%20Trafficking%20of%20a%20Neurotropic%20Virus%20Through%20Inefficient%20Retrograde%20Axonal%20Transport%20and%20the%20Type%20I%20Interferon%20Response.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BPLoS%20Pathogens%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B6%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%283%29%2C%20e1000791.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.ppat.1000791%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.ppat.1000791%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Limited%20Trafficking%20of%20a%20Neurotropic%20Virus%20Through%20Inefficient%20Retrograde%20Axonal%20Transport%20and%20the%20Type%20I%20Interferon%20Response%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Karen%20Z.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lancaster%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Julie%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pfeiffer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gale%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222010-3-5%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.ppat.1000791%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221553-7374%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.ppat.1000791%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T17%3A36%3A39Z%22%7D%7D%5D%7D
Li, M., Li, C., Song, S., Kang, H., Yang, D., & Li, G. (2016). Development and antigenic characterization of three recombinant proteins with potential for Glässer’s disease prevention. Vaccine, 34(19), 2251–2258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.03.014
Cole, L. E., Zhang, J., Kesselly, A., Anosova, N. G., Lam, H., Kleanthous, H., & Yethon, J. A. (2016). Limitations of Murine Models for Assessment of Antibody-Mediated Therapies or Vaccine Candidates against Staphylococcus epidermidis Bloodstream Infection. Infection and Immunity, 84(4), 1143–1149. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.01472-15
Adamo, R. F., Fishbein, I., Zhang, K., Wen, J., Levy, R. J., Alferiev, I. S., & Chorny, M. (2016). Magnetically enhanced cell delivery for accelerating recovery of the endothelium in injured arteries. Journal of Controlled Release, 222, 169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.025
Falendysz, E. A., Lopera, J. G., Lorenzsonn, F., Salzer, J. S., Hutson, C. L., Doty, J., Gallardo-Romero, N., Carroll, D. S., Osorio, J. E., & Rocke, T. E. (2015). Further Assessment of Monkeypox Virus Infection in Gambian Pouched Rats (Cricetomys gambianus) Using In Vivo Bioluminescent Imaging. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 9(10), e0004130. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0004130
Rosen, D. A., Hilliard, J. K., Tiemann, K. M., Todd, E. M., Morley, S. C., & Hunstad, D. A. (2015). Klebsiella pneumoniae FimK Promotes Virulence in Murine Pneumonia. Journal of Infectious Diseases, jiv440. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiv440
Liao, X., Ren, J., Wei, C.-H., Ross, A. C., Cecere, T. E., Jortner, B. S., Ahmed, S. A., & Luo, X. M. (2015). Paradoxical Effects of All-Trans-Retinoic Acid on Lupus-Like Disease in the MRL/lpr Mouse Model. PLOS ONE, 10(3), e0118176. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118176
Caverly, L. J., Caceres, S. M., Fratelli, C., Happoldt, C., Kidwell, K. M., Malcolm, K. C., Nick, J. A., & Nichols, D. P. (2015). Mycobacterium abscessus Morphotype Comparison in a Murine Model. PLOS ONE, 10(2), e0117657. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117657
Palomares, R. A., Sakamoto, K., Walz, H. L., Brock, K. V., & Hurley, D. J. (2015). Acute infection with bovine viral diarrhea virus of low or high virulence leads to depletion and redistribution of WC1+ γδ T cells in lymphoid tissues of beef calves. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 167(3–4), 190–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetimm.2015.07.016
Neishabouri, S. H., Hutson, S. M., & Davoodi, J. (2015). Chronic activation of mTOR complex 1 by branched chain amino acids and organ hypertrophy. Amino Acids, 47(6), 1167–1182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-1944-y
Lopera, J. G., Falendysz, E. A., Rocke, T. E., & Osorio, J. E. (2015). Attenuation of monkeypox virus by deletion of genomic regions. Virology, 475, 129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2014.11.009
Eriksson, A., Williams, M. J., Voisin, S., Hansson, I., Krishnan, A., Philippot, G., Yamskova, O., Herisson, F. M., Dnyansagar, R., Moschonis, G., Manios, Y., Chrousos, G. P., Olszewski, P. K., Frediksson, R., & Schiöth, H. B. (2015). Implication of coronin 7 in body weight regulation in humans, mice and flies. BMC Neuroscience, 16(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-015-0151-9
Zhang, Z., He, L., Hu, S., Wang, Y., Lai, Q., Yang, P., Yu, Q., Zhang, S., Xiong, F., Simsekyilmaz, S., Ning, Q., Li, J., Zhang, D., Zhang, H., Xiang, X., Zhou, Z., Sun, H., & Wang, C.-Y. (2015). AAL exacerbates pro-inflammatory response in macrophages by regulating Mincle/Syk/Card9 signaling along with the Nlrp3 inflammasome assembly. American Journal of Translational Research, 7(10), 1812–1825.
Hyatt, L. D., Wasserman, G. A., Rah, Y. J., Matsuura, K. Y., Coleman, F. T., Hilliard, K. L., Pepper-Cunningham, Z. A., Ieong, M., Stumpo, D. J., Blackshear, P. J., Quinton, L. J., Mizgerd, J. P., & Jones, M. R. (2014). Myeloid ZFP36L1 Does Not Regulate Inflammation or Host Defense in Mouse Models of Acute Bacterial Infection. PLoS ONE, 9(10), e109072. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109072
Bannantine, J. P., Everman, J. L., Rose, S. J., Babrak, L., Katani, R., Barletta, R. G., Talaat, A. M., Grohn, Y. T., Chang, Y.-F., Kapur, V., & Bermudez, L. E. (2014). Evaluation of eight live attenuated vaccine candidates for protection against challenge with virulent Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis in mice. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2014.00088
Palomares, R. A., Hurley, D. J., Woolums, A. R., Parrish, J. E., & Brock, K. V. (2014). Analysis of mRNA expression for genes associated with regulatory T lymphocytes (CD25, FoxP3, CTLA4, and IDO) after experimental infection with bovine viral diarrhea virus of low or high virulence in beef calves. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 37(5–6), 331–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cimid.2014.10.001
Palomares, R. A., Parrish, J., Woolums, A. R., Brock, K. V., & Hurley, D. J. (2014). Expression of toll-like receptors and co-stimulatory molecules in lymphoid tissue during experimental infection of beef calves with bovine viral diarrhea virus of low and high virulence. Veterinary Research Communications, 38(4), 329–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-014-9613-2
Borschensky, C. M., & Reinacher, M. (2014). Mutations in the 3c and 7b genes of feline coronavirus in spontaneously affected FIP cats. Research in Veterinary Science, 97(2), 333–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2014.07.016
Palomares, R. A., Brock, K. V., & Walz, P. H. (2014). Differential expression of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines during experimental infection with low or high virulence bovine viral diarrhea virus in beef calves. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 157(3–4), 149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetimm.2013.12.002
Melero, M., García-Párraga, D., Corpa, J., Ortega, J., Rubio-Guerri, C., Crespo, J., Rivera-Arroyo, B., & Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J. (2014). First molecular detection and characterization of herpesvirus and poxvirus in a Pacific walrus (Odobenus rosmarus divergens). BMC Veterinary Research, 10(1), 968. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-014-0308-2
Erickson, A. K., & Pfeiffer, J. K. (2013). Dynamic Viral Dissemination in Mice Infected with Yellow Fever Virus Strain 17D. Journal of Virology, 87(22), 12392–12397. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02149-13
Wiles, T. J., Norton, J. P., Russell, C. W., Dalley, B. K., Fischer, K. F., & Mulvey, M. A. (2013). Combining Quantitative Genetic Footprinting and Trait Enrichment Analysis to Identify Fitness Determinants of a Bacterial Pathogen. PLoS Genetics, 9(8), e1003716. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003716
Silver, A. C., Dunne, D. W., Zeiss, C. J., Bockenstedt, L. K., Radolf, J. D., Salazar, J. C., & Fikrig, E. (2013). MyD88 Deficiency Markedly Worsens Tissue Inflammation and Bacterial Clearance in Mice Infected with Treponema pallidum, the Agent of Syphilis. PLoS ONE, 8(8), e71388. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071388
Karauzum, H., Adhikari, R. P., Sarwar, J., Devi, V. S., Abaandou, L., Haudenschild, C., Mahmoudieh, M., Boroun, A. R., Vu, H., Nguyen, T., Warfield, K. L., Shulenin, S., & Aman, M. J. (2013). Structurally Designed Attenuated Subunit Vaccines for S. aureus LukS-PV and LukF-PV Confer Protection in a Mouse Bacteremia Model. PLoS ONE, 8(6), e65384. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065384
Chorny, M., Fishbein, I., Tengood, J. E., Adamo, R. F., Alferiev, I. S., & Levy, R. J. (2013). Site-specific gene delivery to stented arteries using magnetically guided zinc oleate-based nanoparticles loaded with adenoviral vectors. The FASEB Journal, 27(6), 2198–2206. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.12-224659
Nichols, D. P., Caceres, S., Caverly, L., Fratelli, C., Kim, S. H., Malcolm, K., Poch, K. R., Saavedra, M., Solomon, G., Taylor-Cousar, J., Moskowitz, S., & Nick, J. A. (2013). Effects of azithromycin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn wound infection. Journal of Surgical Research, 183(2), 767–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2013.02.003
Palomares, R. A., Walz, H. G., & Brock, K. V. (2013). Expression of type I interferon-induced antiviral state and pro-apoptosis markers during experimental infection with low or high virulence bovine viral diarrhea virus in beef calves. Virus Research, 173(2), 260–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2013.02.010
Poulsen, K. P., Faith, N. G., Steinberg, H., & Czuprynski, C. J. (2013). Bacterial load and inflammation in fetal tissues is not dependent on IL-17a or IL-22 in 10–14 day pregnant mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes. Microbial Pathogenesis, 56, 47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2012.11.003
Hanstein, R., Negoro, H., Patel, N. K., Charollais, A., Meda, P., Spray, D. C., Suadicani, S. O., & Scemes, E. (2013). Promises and pitfalls of a Pannexin1 transgenic mouse line. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2013.00061
Austin, W. R., Armijo, A. L., Campbell, D. O., Singh, A. S., Hsieh, T., Nathanson, D., Herschman, H. R., Phelps, M. E., Witte, O. N., Czernin, J., & Radu, C. G. (2012). Nucleoside salvage pathway kinases regulate hematopoiesis by linking nucleotide metabolism with replication stress. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 209(12), 2215–2228. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20121061
Kumar, M., Roe, K., Nerurkar, P. V., Namekar, M., Orillo, B., Verma, S., & Nerurkar, V. R. (2012). Impaired Virus Clearance, Compromised Immune Response and Increased Mortality in Type 2 Diabetic Mice Infected with West Nile Virus. PLoS ONE, 7(8), e44682. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0044682
Adhikari, R. P., Karauzum, H., Sarwar, J., Abaandou, L., Mahmoudieh, M., Boroun, A. R., Vu, H., Nguyen, T., Devi, V. S., Shulenin, S., Warfield, K. L., & Aman, M. J. (2012). Novel Structurally Designed Vaccine for S. aureus α-Hemolysin: Protection against Bacteremia and Pneumonia. PLoS ONE, 7(6), e38567. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038567
Bessen, R. A., Robinson, C. J., Seelig, D. M., Watschke, C. P., Lowe, D., Shearin, H., Martinka, S., & Babcock, A. M. (2011). Transmission of Chronic Wasting Disease Identifies a Prion Strain Causing Cachexia and Heart Infection in Hamsters. PLoS ONE, 6(12), e28026. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028026
Smith, J. S., Xu, Z., Tian, J., Palmer, D. J., Ng, P., & Byrnes, A. P. (2011). The Role of Endosomal Escape and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Adenoviral Activation of the Innate Immune Response. PLoS ONE, 6(10), e26755. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026755
Gogal, Jr., R. M., Kerr, R., Kingsley, D. H., Granata, L. A., LeRoith, T., Holliman, S. D., Dancho, B. A., & Flick, Jr., G. J. (2011). High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing of Murine Norovirus 1–Contaminated Oysters Inhibits Oral Infection in STAT-1<SUP>-/-</SUP>–Deficient Female Mice. Journal of Food Protection, 74(2), 209–214. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-10-235
Rayner, K. J., Suarez, Y., Davalos, A., Parathath, S., Fitzgerald, M. L., Tamehiro, N., Fisher, E. A., Moore, K. J., & Fernandez-Hernando, C. (2010). MiR-33 Contributes to the Regulation of Cholesterol Homeostasis. Science, 328(5985), 1570–1573. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1189862
Lancaster, K. Z., & Pfeiffer, J. K. (2010). Limited Trafficking of a Neurotropic Virus Through Inefficient Retrograde Axonal Transport and the Type I Interferon Response. PLoS Pathogens, 6(3), e1000791. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000791






